Understanding Scattered Spider & Recommendations for Resilience-Building
Scattered Spider is a highly adaptive, financially motivated cybercriminal group representing a significant and evolving threat to global enterprises. The group’s sophisticated social engineering, advanced identity system compromise, and "living off the land" (LOtL) tactics have enabled it to execute high-impact ransomware and data extortion campaigns across diverse sectors, including gaming, retail, airlines, and insurance. The financial and reputational consequences of their attacks are exemplified by disruption and multi-million dollar losses experienced by major global brands and underscore the critical need for robust cyber resilience capabilities.
reportUnderstanding Scattered Spider & Recommendations for Resilience-Building
Scattered Spider is a highly adaptive, financially motivated cybercriminal group representing a significant and evolving threat to global enterprises. The group’s sophisticated social engineering, advanced identity system compromise, and "living off the land" (LOtL) tactics have enabled it to execute high-impact ransomware and data extortion campaigns across diverse sectors, including gaming, retail, airlines, and insurance. The financial and reputational consequences of their attacks are exemplified by disruption and multi-million dollar losses experienced by major global brands and underscore the critical need for robust cyber resilience capabilities.
reportThe speed at which Scattered Spider operates, with breakout times often measured in minutes rather than hours, demands an accelerated defensive posture. Traditional security paradigms are increasingly insufficient against adversaries who exploit human vulnerabilities and legitimate system functionalities. This report details Scattered Spider's modus operandi, explores emblematic attacks, and quantifies the urgency through key cybersecurity metrics.
Effective defense against Scattered Spider necessitates a holistic, multi-layered strategy. This includes strengthening identity and access management, enhancing social engineering defenses, adhering to cloud security best practices, and implementing proactive incident response and recovery preparedness.
The group’s success in undermining technical security controls affirms the need for strong data security and recovery capabilities to mitigate post-compromise impact through immutable data protection, AI-driven anomaly detection, and rapid, orchestrated recovery as elements of a well-rounded, defense-in-depth strategy.
Who is Scattered Spider?
Scattered Spider (aka UNC3944, Roasted 0ktapus, Scatter Swine, Muddled Libra, Octo Tempest, Storm-0971, DEV-0971, and Starfraud1) pursues financial gain through a range of lucrative cybercriminal activities including the theft of sensitive data, cryptocurrency stealing, data exfiltration, and extortion with ransomware. CrowdStrike categorizes Scattered Spider as an "eCrime" adversary, distinguishing them from nation-state advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Operational since at least mid-2022, Scattered Spider has evolved considerably over time. Initially primarily an initial access broker specializing in phishing and social engineering, it has since expanded into a full-fledged ransomware affiliate, leveraging various Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) platforms, indicating integration into the broader cybercriminal ecosystem. Scattered Spider operators are predominantly young adults based in Western countries with fluency in local dialects.

Scattered Spider's categorization by some analysts as a "financially motivated advanced persistent threat (APT)" carries significant implications. Blurring traditional lines between cybercrime and state-level espionage or sabotage indicates its tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) make it capable not only of financial crime but also of conducting complex, sustained campaigns.
Scattered Spider does not act in isolation. It operates within a global hacking collective sometimes known as "the Community" or "the Com". This often overlooked detail illustrates a support structure that facilitates the rapid sharing of TTPs, exploits, tools, initial access vectors, and potentially specialized skills or resources among members. This aids adaptability and resilience to disruption by law enforcement as tactics are disseminated and refined within this network.
Scattered Spider TTPs
Social Engineering Mastery
Scattered Spider's primary initial access vector involves sophisticated social engineering with a diverse array of tactics. These include forms of phishing including smishing (SMS phishing), the use of domain name look-alikes, push bombing (a technique capitalizing on multi-factor authentication fatigue), and SIM swap attacks.
The group frequently impersonates company IT or helpdesk staff, employees in distress, or even executives to coerce individuals into divulging credentials, installing remote access tools, or bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA). Its success is fundamentally rooted in exploiting human psychology, particularly the responsiveness, helpfulness, and inherent empathy of IT support teams that are often under pressure to resolve issues quickly. An example of this is the use of help desk social engineering to reset MFA for highly privileged IT users during the costly MGM and Caesars attacks.

Scattered Spider's success is not dependent on discovering zero-day software vulnerabilities, but rather on a profound understanding of human psychology and organizational processes.
This means technical solutions alone are insufficient. Instead, organizations must invest in human-centric security measures, including continuous, adaptive security awareness training and robust procedural controls for sensitive operations.
Initial Access & Privilege Escalation
Beyond social engineering, Scattered Spider skillfully exploits compromised Okta identity credentials and MFA codes to establish initial footholds within target environments. "Living off the Land and Cloud" (LotL/LotC) techniques allow for the abuse of legitimate, built-in administrative tools (e.g., PowerShell, Task Scheduler), SaaS services (e.g., cloud file storage, notebook platforms), and identity workflows within cloud environments. This often includes leveraging misconfigurations and native features to escalate privileges and maintain persistence.
One advanced technique involves Bring-Your-Own-Vulnerable-Driver (BYOVD) attacks, in which the group loads signed but outdated drivers to disable and evade Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions. It also engages in session proxy interception, abusing services to capture temporary tokens during help desk resets and replaying them for elevated access. Cloud identity and federation abuse tactics include inserting rogue Identity Providers (IdPs) into corporate Single Sign-On (SSO) systems and tampering with cloud audit logs (e.g., AWS CloudTrail) to erase evidence of unauthorized trust relationships.
The extensive use of LotL techniques is a deliberate strategy to avoid detection. By using legitimate tools and cloud services present in the victim's environment, Scattered Spider's activities blend seamlessly with normal network and cloud operations. This allows for lateral movement and privilege escalation without deploying easily detectable malware. Organizations must therefore shift towards advanced behavioral analytics, robust Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), and continuous monitoring of cloud identity and access logs to identify anomalous patterns in legitimate tool usage.
Ransomware & Data Extortion
Scattered Spider has solidified its role as a significant player in the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) ecosystem, affiliating with prominent variants such as ALPHV (BlackCat), RansomHub, Qilin, and DragonForce. It frequently employs double extortion, where sensitive data is stolen and public disclosure is threatened as leverage, even in instances where encryption does not occur.
The group’s technical capabilities also extend to hypervisor encryption, where they access virtualization administration interfaces to encrypt entire ESXi clusters simultaneously. They have also been observed utilizing Post-Exfiltration File Encryption.
Notable Attacks
Scattered Spider has been linked to numerous high-profile cyberattacks, each demonstrating their evolving capabilities and the severe
consequences for victims.
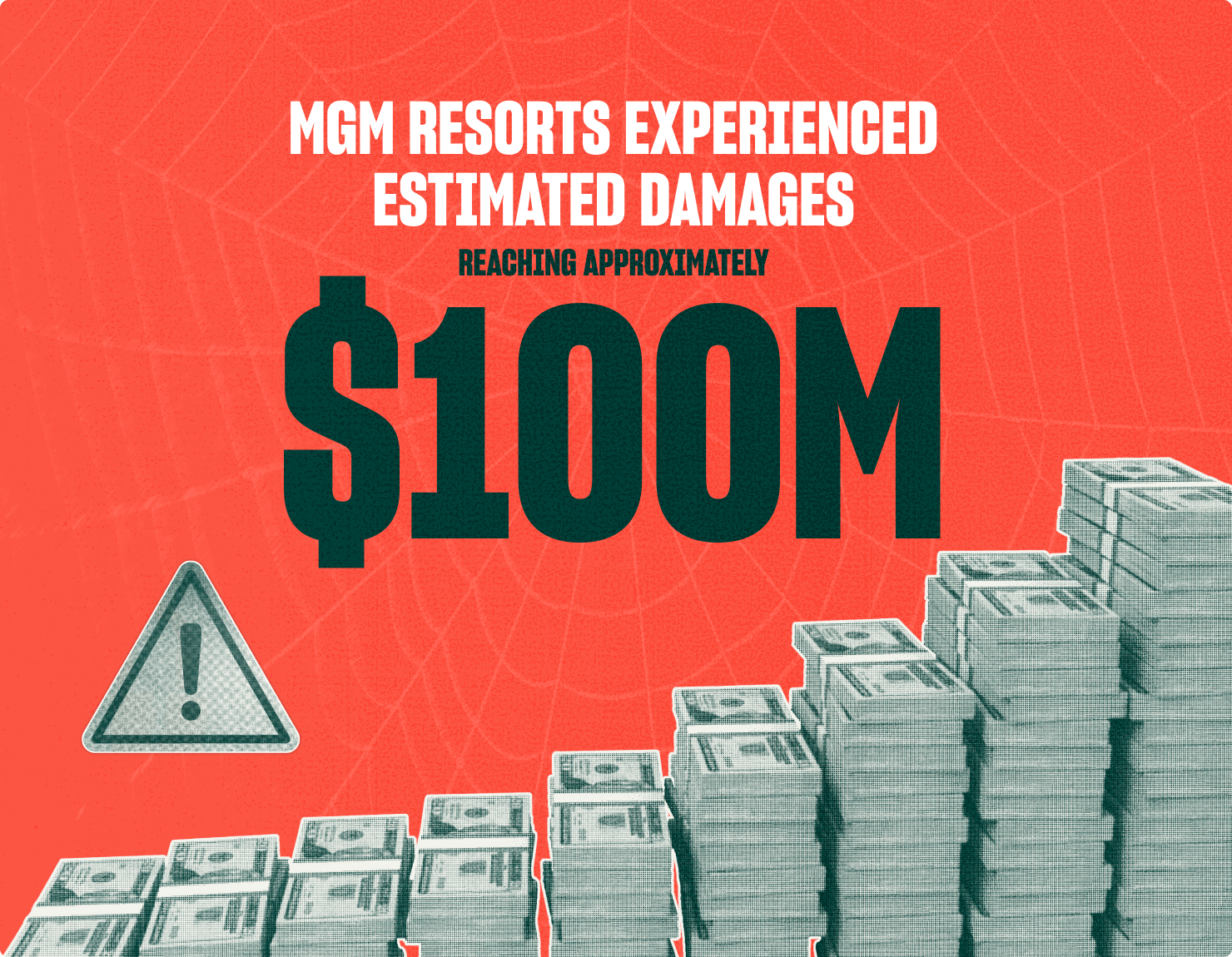
- MGM Resorts and Caesars Entertainment (September 2023): MGM Resorts experienced a 10-day disruption of its critical IT systems, substantial exfiltration of customer data and PII, with estimated damages reaching approximately $100 million. The CEO publicly acknowledged that the hack caused the company to be "completely in the dark" about its properties. Caesars Entertainment, facing similar tactics, paid a $15 million ransom after Scattered Spider accessed driver's license numbers and potentially Social Security numbers for a "significant number" of customers. Both attacks involved help desk social engineering to bypass MFA for highly privileged IT users. Consequences included class-action lawsuits against both companies and a notable drop in stock prices.
- UK Retailers (Late April 2025):
Scattered Spider leveraged DragonForce ransomware for ransomware attacks on major UK retailers. The Marks & Spencer breach alone reportedly caused "hundreds of millions in lost profits." These incidents resulted in significant operational disruptions, reputational loss, and data loss.
- Insurance Sector (June 2025):
Multiple U.S.-based insurance companies, including Erie Insurance, were impacted by attacks attributed to Scattered Spider. These attacks targeted the sector due to its "vast repositories of sensitive personal and financial data" and often "outdated security infrastructures." Thousands of customers also reported losing access to essential services.
- Airlines (US and Canada, July 2025):
The FBI and technology companies issued alerts warning aviation companies after Scattered Spider targeted airlines. Qantas Airlines, for instance, reported that a "significant" amount of customer data was likely stolen from its records during a cyberattack.
Because the group exploits common, human-centric weaknesses through social engineering and identity system compromise, it is not constrained by industry specialization. Its ability to quickly identify and pivot to new high-value targets also highlights effective reconnaissance and intelligence-gathering capabilities.
The severe financial and operational fallout from these incidents is a direct consequence of the attackers' ability to leverage compromised identities for rapid lateral movement, privilege escalation, data exfiltration, and ransomware deployment. This reinforces the paramount need for robust identity governance, privileged access management (PAM), and continuous, real-time monitoring of all authentication and authorization activities.
FINANCIAL AND REPUTATIONAL IMPACT
The financial and reputational repercussions of Scattered Spider's operations are substantial and multifaceted, extending far beyond immediate ransom payments.
The most significant costs stem from prolonged operational downtime, the extensive resources required for incident response and recovery, legal fees from class-action lawsuits, and the intangible, long-term damage to brand reputation and customer trust. Organizations must therefore prioritize comprehensive cyber resilience and rapid recovery capabilities as much as, if not more than, preventative measures given that "the cost of comprehensive security implementation pales in comparison to the operational, financial, and reputational damage caused by successful cyberattacks," according to one advisory firm.
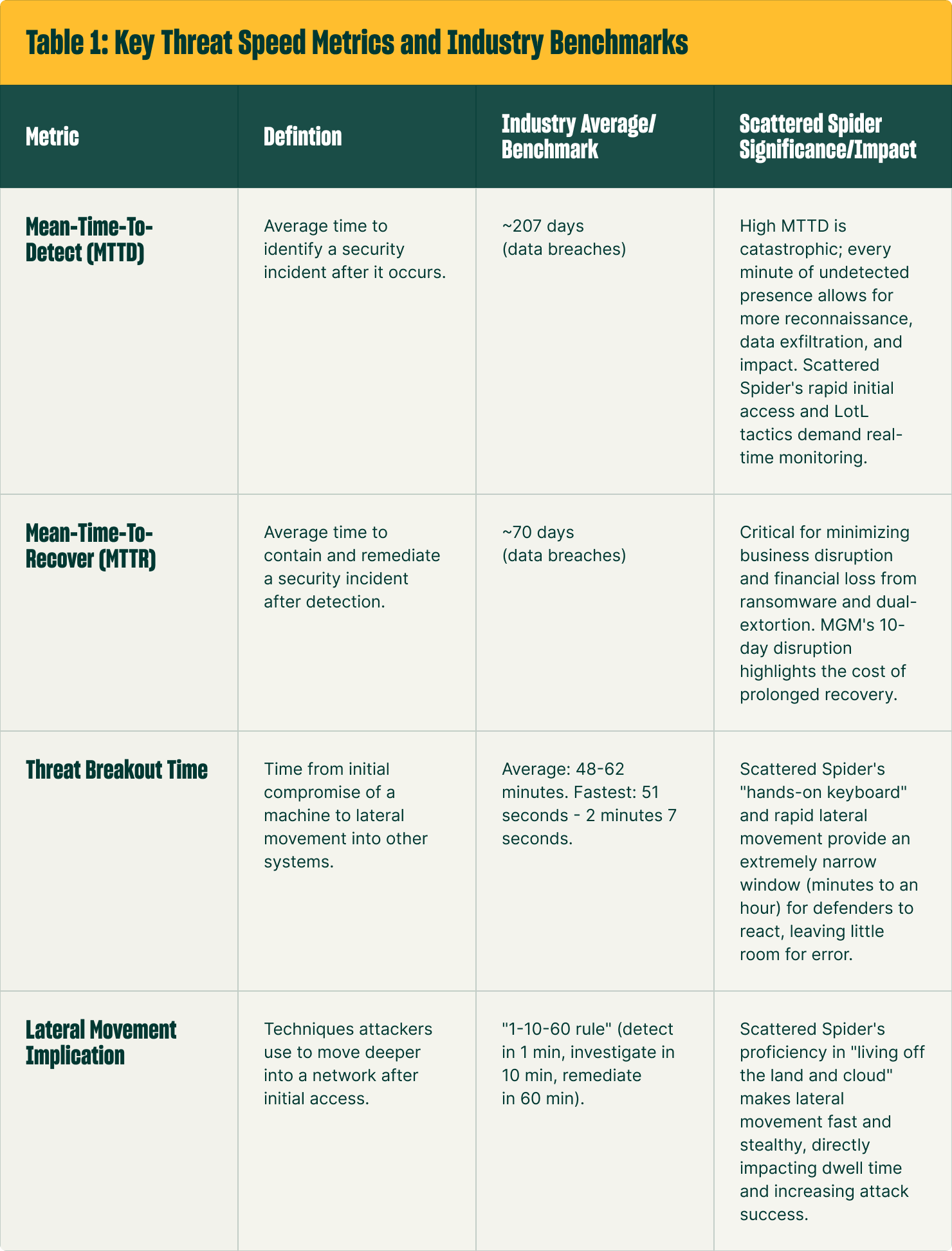
Understanding the speed at which threat actors operate is essential for effective defense. Scattered Spider's rapid operational tempo underscores the critical importance of minimizing Mean-Time-To-Detect (MTTD), Mean-Time-To-Recover (MTTR), and threat breakout time. As shown in Table 1, reducing the time spent at each stage limits the total damage threat groups like Scattered Spider are able to inflict.

Countering an adaptive and sophisticated adversary like Scattered Spider requires a multi-layered, defense-in-depth strategy addressing not only technical vulnerabilities but also the human element and the entire
attack lifecycle.
STRENGTHENING IDENTITY AND ACCESS MANAGEMENT (IAM)
Robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) is foundational. Organizations must implement strong, phishing-resistant MFA methods like FIDO2 keys, number matching, and geo-verification. Where feasible, transitioning to passwordless authentication with solutions like passkeys can significantly reduce the risk of credential compromise.
Enforcing Just-In-Time (JIT) access is critical, granting privileged access only for specific durations and with the minimum necessary permissions. Strict adherence to the principle of least privilege means users and systems have only the necessary permissions for their job roles, with regular audits of access rights.
Implementing robust Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools to query MFA activity, track unusual logins , and meticulously review help desk tickets for suspicious password resets or account lockouts, can provide early warning. For sensitive requests like password resets or MFA registration, mandating out-of-band verification—such as a call-back to a registered number or confirmation via a known corporate email address—adds a crucial layer of security.
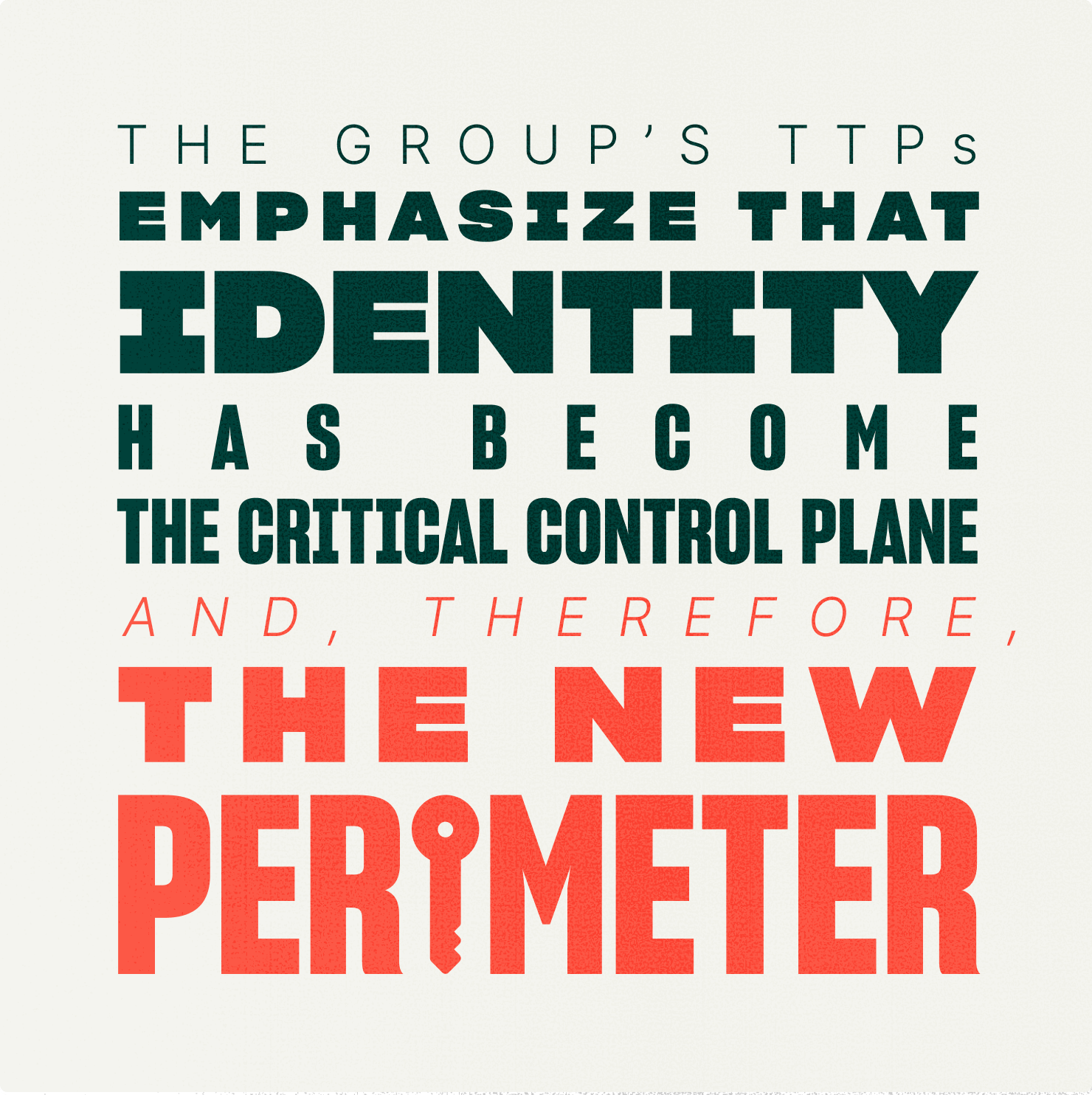
Investment should shift from solely network-centric defenses to comprehensive identity governance, privileged access management, and advanced authentication solutions. A compromised identity now represents a direct, often undetected, path to an organization's most critical assets, making it the most vital control point.
ENHANCED SOCIAL ENGINEERING DEFENSE
Enhanced social engineering defense is critical given Scattered Spider's reliance on human manipulation. Organizations must develop and implement comprehensive, ongoing security awareness training educating employees on how cybercriminals operate, key red flags, and common advanced social engineering tactics like smishing, vishing, and multi-vector social engineering. Gone are the days of advising users to simply scan suspicious emails for typos or unfamiliar senders.
Implementing clear, strict policies for high-risk procedures, such as financial transfers or sensitive data access, is also crucial. For example, mandating face-to-face or multi-channel confirmation for financial transfers exceeding a certain amount can prevent CEO fraud.
Finally, fostering a zero-trust communication approach where employees are encouraged to question and verify unusual or urgent requests, even if they appear to come from trusted sources, is essential.
Cloud Security Best Practices
Zero trust architecture is critical in cloud environments. No user or device should be automatically trusted and every access request thoroughly verified. Segmenting networks to isolate resources and limit lateral movement is a key zero trust component. Continuously monitoring cloud environments for vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and deviations from security best practices is essential.
PROACTIVE INCIDENT RESPONSE AND
RECOVERY PREPAREDNESS
Proactive incident response and robust recovery preparedness can help minimize the impact of a successful compromise, but comprehensive incident response plans must be thoughtfully designed and regularly updated. Plans should include clear steps for containment, securing privileged accounts, eradicating persistence, removing privilege escalation, verifying cleanliness, and restoring operations from clean backups.
Regular tabletop exercises and crisis simulations are vital to validating recovery plans, ensuring preparedness, and identifying gaps before a real attack. Ensuring offline backups are tested and readily available is a
critical component.
Holistic defense strategies encompass a wide array of controls, from human-centric to technical, that cannot function in isolation. MFA can be undermined if help desk procedures can be socially engineered to reset it. Advanced EDR can be bypassed if BYOVD techniques are not addressed. MTTD can soar if LotL techniques go unnoticed. Any comprehensive strategy requires a synchronized, layered approach for countering an adaptive adversary that probes for the weakest link across multiple domains.

Modern data security requires a focus on adversarial threats like ransomware rather than solely on preventing traditional operational failures. Architecture that addresses the challenges posed by adaptable threat groups like Scattered Spider quickly proves its value post-compromise by allowing organizations to recover key capabilities and resume
operations quickly.
Immutable Data Protection
Organizations must ensure data integrity in the face of ransomware attacks through air-gapped, immutable backups. This data, once backed up, cannot be altered, encrypted, or deleted by attackers, even if they gain control of the production environment. "Air-gapped" backups are logically isolated from the production environment, even if the primary network is compromised. This is critical because Scattered Spider often deploys ransomware or engages in post-exfiltration file encryption. Data integrity should periodically validate immutability, ensuring backup reliability.
Zero trust design principles should validate data with integrity checks, securing backups from malicious actors.
In the common advice, "never trust, always verify:"
- Retention lock prevents the premature deletion or modification of snapshots and backup data for a specified duration, essentially not implicitly trusting commands to delete snapshots or perform factory resets, for example.
- Quorum authentication mandates additional verifications by requiring multiple approvals before certain data-modifying or critical system actions can be performed.
These zero trust-inspired capabilities are crucial against Scattered Spider's ransomware and data tampering tactics.
AI-Driven Anomaly Detection
AI-driven early detection capabilities leverage machine learning to identify ransomware and other anomalies before they cause widespread damage. Continuous inline scanning of data across on-premises, in the cloud, and across SaaS environments should integrate with threat intelligence feeds to identify potential threats proactively based on metrics like change rates, abnormal system sizes, entropy changes, and VM-level encryption detection. Anomalies should generate alerts via native UI, email, or integration with SOAR/SIEM applications to reduce MTTR by identifying suspicious behavior in backup data.
Rapid and Orchestrated Cyber Recovery
Rapid incident response and recovery capabilities accelerate the process of restoring operations to a clean state with minimal downtime and data loss. Using pre-computed hashing techniques to identify clean recovery points without time-consuming rehydration speeds the pinpointing of a safe point to restore from.
Orchestrated cyber recovery should integrate with commonly used environments like Azure VMs and provide guided workflows for granular or bulk recovery of applications, files, or objects. This should include the ability to recover the most recent data workloads first to minimize downtime. Orchestrated cyber recovery must be testable, with the ability to perform crisis simulations to ensure preparedness and validate recovery plans in isolated environments.
These capabilities directly contribute to reducing the MTTR, providing early warnings and granular visibility into what data was impacted and how it changed over time.
Hybrid Identity Recovery
A significant percentage of cyberattacks involve compromised credentials, so comprehensive identity recovery capabilities must streamline Active Directory (AD) recovery, reducing complex manual steps to a simplified, wizard-driven approach. The alternative could mean weeks-long, error-prone AD restoration and the associated downtime. Integrated solutions orchestrate both identity and data recovery, which is vital given Scattered Spider's focus on identity compromise.
Sensitive Data Risk Identification
Organizations must be able to identify sensitive data risk, reducing exposure through data discovery, classification, and access governance capabilities. Scanning backups for sensitive data can help proactively mitigate attack impact and facilitate compliance with regulations like GDPR, PCI-DSS, and HIPAA, complete with insights into what regulatory bodies may need to be notified if certain data types are impacted.

Scattered Spider represents a formidable and evolving threat, characterized by its mastery of social engineering, sophisticated identity-based attacks, and financially motivated operations. The group's ability to pivot across diverse industries and leverage "living off the land" techniques, coupled with the shrinking window for detection and response, demands a fundamental shift in defensive strategies.
The significant financial and reputational damages incurred by their victims underscore that the true cost of a breach extends far beyond direct ransom payments, encompassing prolonged operational disruption, legal liabilities, and erosion of trust. The concern that Scattered Spider's "playbook" could be adopted by nation-state actors further elevates the urgency for robust defenses across all critical infrastructure.
To effectively counter Scattered Spider and similar adaptive adversaries, organizations must adopt a holistic, multi-layered defense-in-depth approach. This approach must recognize that identity has become the new perimeter, and the human element remains the most exploitable attack surface.
Key Recommendations:
- Prioritize Identity and Access Management (IAM) Hardening: Implement phishing-resistant MFA (e.g., FIDO2 keys) and explore passwordless authentication. Enforce Just-In-Time (JIT) access and the principle of least privilege across all user accounts and systems. Crucially, establish continuous, real-time monitoring of all identity and authentication logs to detect anomalous behavior, and mandate out-of-band verification for all high-risk identity changes.
- Invest in Human-Centric Security:
Develop and maintain a comprehensive, adaptive security awareness training program that educates employees on the latest social engineering tactics, including AI-enhanced deepfakes and hyper-personalized phishing. Regularly conduct multi-vector social engineering simulations to test and reinforce employee vigilance. Implement strict policies for sensitive procedures, requiring multi-channel verification for actions like financial transfers.
- Strengthen Cloud Security Posture:
Adopt zero trust architecture across all cloud environments, enforcing strict segmentation and continuous verification for every access request. Implement robust Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and automated vulnerability scanning to identify and remediate misconfigurations. Ensure secure configurations for containerized and serverless environments, adhering to the shared responsibility model.
- Accelerate Detection and Response Capabilities:
Deploy advanced Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) or Extended Detection and Response (XDR) solutions capable of real-time behavioral analytics to detect "living off the land" activities, lateral movement, and attempts to disable security software (e.g., BYOVD). Implement robust logging and continuous monitoring across all IT and cloud infrastructure to reduce Mean-Time-To-Detect (MTTD) to minutes, not days.
- Build Resilient Data Recovery Mechanisms:
Implement immutable backup solutions that ensure data cannot be altered, encrypted, or deleted by ransomware or malicious insiders. Develop and regularly test comprehensive incident response and cyber recovery plans, including full-scale recovery simulations in isolated environments. Focus on reducing Mean-Time-To-Recover (MTTR) by enabling rapid, orchestrated restoration of critical systems and data to a clean state.
Backup and recovery capabilities represent a critical component of comprehensive defense. Immutable backups, AI-driven anomaly detection on backup data, and orchestrated recovery capabilities directly mitigate the impact of Scattered Spider's ransomware and data extortion tactics, significantly reducing MTTR.
Identity recovery solutions are critical for restoring compromised Active Directory environments. Hardening data resilience and bolstering recovery capabilities are critical components of a broad security ecosystem that includes robust IAM solutions, advanced endpoint and network security, and continuous human-centric training to build a truly resilient defense against sophisticated, adaptive adversaries like Scattered Spider.